In-Depth Ab Initio Study of Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence in 4,5-Di(9H-carbazol-9-yl)-phthalonitrile
By Alexandra Ya. Freidzon and Alexander A. Bagaturyants
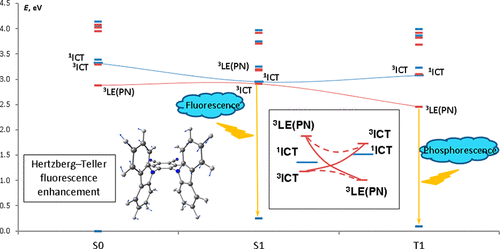
Molecules capable of thermally activated delayed fluorescence (TADF) are promising as emitters in organic light-emitting devices. Processes leading to and competing with TADF in 4,5-di(9H-carbazol-9-yl)-phthalonitrile are analyzed in detail. It is demonstrated that the key features of an efficient TADF emitter include the presence of two triplet states of different natures with potential energy surfaces crossing between the T1 and S1 minima and a noticeable dependence of the S1 → S0 oscillator strength on molecular deformations from low-frequency antisymmetric vibrational modes. These conclusions can be useful in the targeted design of efficient TADF emitters.